Detección Preventiva de la Somnolencia del Conductor a partir de Señales EEG Mediante Sistemas Expertos Difusos
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17488/RMIB.45.1.1Palabras clave:
electroencefalograma, detección de somnolencia, sistemas expertos, somnolencia en la conducciónResumen
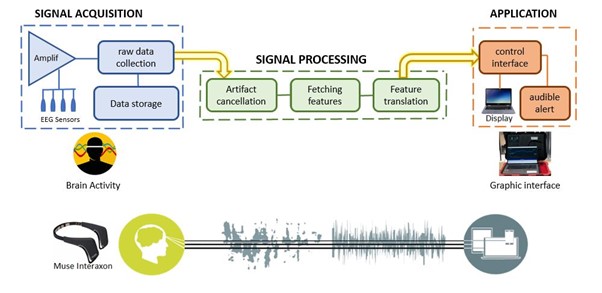
Actualmente, el porcentaje de accidentes de tráfico ha aumentado, y según las estadísticas, este porcentaje seguirá aumentando cada año, por lo que es necesario desarrollar nuevas tecnologías para prevenir este tipo de accidentes. Este trabajo presenta un sistema de detección de somnolencia basado en señales de electroencefalograma (EEG) utilizando un par de canales (Fp1 y Fp2) aplicado a los conductores antes de entrar en sus vehículos. En primer lugar, este modelo detecta la relación entre el área bajo la curva (AUC) de las ondas cerebrales alfa, un parámetro eficaz para detectar la somnolencia. A continuación, la información extraída se pasa a un sistema experto difuso (FES) que clasifica el estado del sujeto como "alerta" o "somnoliento"; el criterio utilizado fue un umbral y el entrenamiento con niveles subjetivos. El sistema propuesto se comparó con modelos de redes neuronales, como la máquina de vectores de soporte (SVM), K vecinos más cercanos (KNN) y el bosque aleatorio (RF). Se realizaron mediciones de ciento veinte minutos en cada uno de los diez conductores durante dos días para probar el sistema. Las pruebas confirman que este sistema es adecuado para las medidas preventivas y que el sistema difuso es superior a los métodos tradicionales de redes neuronales.
Descargas
Citas
World Health Organization, “Global status report on road safety 2018,” WHO. France, 2018 Accessed: Dec. 21, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241565684
Pan American Health Organization, World Health Organization, “Road Safety,” PAHO/WHO. Accessed: Dec. 21, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.paho.org/en/topics/road-safety
D. Carhuavilca, Perú: Natalidad, Mortalidad y Nupcialidad, 2019, Lima, Perú: Instituto Nacional de Informática y Estadística, 2020. [Online]. Available: https://www.inei.gob.pe/media/MenuRecursivo/publicaciones_digitales/Est/Lib1766/libro.pdf
Policía Nacional del Perú, “Muertos por Accidentes de Tránsito 2006 – 2017,” Ministerio de transportes y Comunicaciones. Accessed: Dec. 21, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.mtc.gob.pe/cnsv/documentos/muertosAccidenteTransito_2006-2017.pdf.
E. Huerta. “La preocupante cifra de muertes por accidentes de tránsito en el Perú y sus principales causas.” El Comercio Perú. https://elcomercio.pe/tecnologia/actualidad/preocupante-cifra-muertes-accidentes-transito-peru-principales-causas-ecpm-noticia-651076-noticia/ (accessed Dec. 21, 2023).
J. Rey de Castro, “Drowsy drivers on the roads of Peru: findings and proposals,” Rev. Med. Hered., vol. 22, no. 4, pp. 155–156, Oct. 2011. [Online]. Available: http://www.scielo.org.pe/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1018-130X2011000400001
A. A. Putilov and O. G. Donskaya, “Construction and validation of the EEG analogues of the Karolinska sleepiness scale based on the Karolinska drowsiness test,” Clin. Neurophysiol., vol. 124, no. 7, pp. 1346–1352, Jul. 2013, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2013.01.018
V. Riethmeister, R. W. Matthews, D. Dawson, M. R. de Boer, S. Brouwer, and U. Bültmann, “Time-of-day and days-on-shift predict increased fatigue over two-week offshore day-shifts,” Appl. Ergon., vol. 78, pp. 157–163, Jul. 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apergo.2019.02.010
A. Sahayadhas, K. Sundaraj, and M. Murugappan, “Detecting Driver Drowsiness Based on Sensors: A Review,” Sensors, vol. 12, no. 12, pp. 16937–16953, Dec. 2012, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/s121216937
V. Bajaj, S. Taran, S. K. Khare, and A. Sengur, “Feature extraction method for classification of alertness and drowsiness states EEG signals,” Appl. Acoust., vol. 163, art. no. 107224, Jun. 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apacoust.2020.107224
U. Budak, V. Bajaj, Y. Akbulut, O. Atila, and A. Sengur, “An Effective Hybrid Model for EEG-Based Drowsiness Detection,” IEEE Sens. J., vol. 19, no. 17, pp. 7624–7631, Sep. 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/jsen.2019.2917850
M. Fernandes, “Driver drowsiness detection using non-intrusive eletrocardiogram and steering wheel angle signals,” M. S. thesis, Univ. Porto, Porto, Portugal, 2019. [Online]. Available: https://repositorio-aberto.up.pt/bitstream/10216/122936/2/358726.pdf
S. Arefnezhad, S. Samiee, A. Eichberger, and A. Nahvi, “Driver Drowsiness Detection Based on Steering Wheel Data Applying Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Feature Selection,” Sensors, vol. 19, no. 4, art. no. 943, Feb. 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/s19040943
M. Chai, s.-w. Li, w.-c. Sun, m.-z. Guo, and m.-y. Huang, “Drowsiness monitoring based on steering wheel status,” Transp. Res. D Transp. Environ., vol. 66, pp. 95–103, Jan. 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2018.07.007
C. Fors, C. Ahlström, P. Sörner, J. Kovaceva, et al., “Camera-based sleepiness detection Final report of the project SleepEYE,” Virtual Prototyping and Assessment by Simulation, 2011. Accessed: Aug. 23, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:674103/FULLTEXT01.pdf
M. H. Baccour, F. Driewer, E. Kasneci, and W. Rosenstiel, “Camera-Based Eye Blink Detection Algorithm for Assessing Driver Drowsiness,” in 2019 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Paris, France, 2019, pp. 987-993, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ivs.2019.8813871
T. Azim, M. A. Jaffar, and A. M. Mirza, “Fully automated real time fatigue detection of drivers through Fuzzy Expert Systems,” Appl. Soft Comput., vol. 18, pp. 25–38, May 2014, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2014.01.020.
V. Vijayan and E. Sherly, “Real time detection system of driver drowsiness based on representation learning using deep neural networks,” J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst., vol. 36, no. 3, pp. 1977–1985, Mar. 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.3233/jifs-169909
B.-G. Lee, B.-L. Lee, and W.-Y. Chung, “Mobile Healthcare for Automatic Driving Sleep-Onset Detection Using Wavelet-Based EEG and Respiration Signals,” Sensors, vol. 14, no. 10, pp. 17915–17936, Sep. 2014, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/s141017915
Y. Jiao, Y. Deng, Y. Luo, and B.-L. Lu, “Driver sleepiness detection from EEG and EOG signals using GAN and LSTM networks,” Neurocomputing, vol. 408, pp. 100–111, Sep. 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2019.05.108
Y. Jiao and B.-L. Lu, “Detecting driver sleepiness from EEG alpha wave during daytime driving,” in 2017 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), Kansas City, MO, USA, 2017, pp. 728-731, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/BIBM.2017.8217744
Y. Jiao and B.-L. Lu, “An alpha wave pattern from attenuation to disappearance for predicting the entry into sleep during simulated driving,” in 2017 8th International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering (NER), Shanghai, China, 2017, pp. 21-24, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/NER.2017.8008282
A. A. Putilov and O. G. Donskaya, “Alpha attenuation soon after closing the eyes as an objective indicator of sleepiness,” Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol., vol. 41, no. 12, pp. 956–964, Dec. 2014, doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/1440-1681.12311
S.-C. Ng and P. Raveendran, “EEG Peak Alpha Frequency as an Indicator for Physical Fatigue,” in 11th Mediterranean Conference on Medical and Biomedical Engineering and Computing 2007. IFMBE Proceedings, vol 16. Springer, Heidelberg, Germany, 2007, pp. 517–520, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-73044-6_132
S. Hanslmayr, J. Gross, W. Klimesch, and K. L. Shapiro, “The role of alpha oscillations in temporal attention,” Brain Res. Rev., vol. 67, no. 1–2, pp. 331–343, Jun. 2011, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresrev.2011.04.002
J. Katona, I. Farkas, T. Ujbanyi, P. Dukan, and A. Kovari, “Evaluation of the NeuroSky MindFlex EEG headset brain waves data,” in 2014 IEEE 12th International Symposium on Applied Machine Intelligence and Informatics (SAMI), Herl'any, Slovakia, 2014, pp. 91-94, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/SAMI.2014.6822382
M. Pathak and A. K. Jayanthy, “Designing of a single channel EEG acquisition system for detection of drowsiness,” in 2017 International Conference on Wireless Communications, Signal Processing and Networking (WiSPNET), Chennai, India, 2017, pp. 1364-1368, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/WiSPNET.2017.8299986
M. Pathak and A. K. Jayanthy, “Development of a Real- Time Single Channel Brain–Computer Interface System for Detection of Drowsiness,” Biomed. Eng. Appl. Basis Commun., vol. 29, no. 3, art no. 1750019, Jun. 2017, doi: https://doi.org/10.4015/s1016237217500193
D. L. Schomer, “The Normal EEG in an Adult,” in The Clinical Neurophysiology Primer, A. S. Blum, S. B. Rutkove, Eds., Totowa, NJ, USA: Humana Press eBooks, 2007, ch. 5, pp. 57–71, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59745-271-7_5
S.-H. Hwang, M. Park, J. Kim, Y. Yun, and J. Son, “Driver Drowsiness Detection Using EEG Features,” in HCI International 2018 – Posters' Extended Abstracts. HCI 2018. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol. 852, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2018, pp. 367-374, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-92285-0_49
C. Dissanayaka, E. Ben-Simon, M. Gruberger, A. Maron-Katz, H. Sharon, T. Hendler, D. Cvetkovic, “Comparison between human awake, meditation and drowsiness EEG activities based on directed transfer function and MVDR coherence methods,” Med. Biol. Eng. Comput., vol. 53, no. 7, pp. 599–607, Jul. 2015, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-015-1272-0
R. Vallat, M. Eskinazi, A. Nicolas, and P. Ruby, “Sleep and dream habits in a sample of French college students who report no sleep disorders,” J. Sleep Res., vol. 27, no. 5, art. no. e12659, Feb. 2018, doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/jsr.12659
E. Combrisson, R. Vallat, C. O'Reilly, M. Jas, et al., “Visbrain: A Multi-Purpose GPU-Accelerated Open-Source Suite for Multimodal Brain Data Visualization,” Front. Neuroinform., vol. 13, art. no. 14, Mar. 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fninf.2019.00014
P. A. M. Kanda, E. F. Oliveira, and F. J. Fraga, “EEG epochs with less alpha rhythm improve discrimination of mild Alzheimer’s,” Comput. Methods Programs Biomed., vol. 138, pp. 13–22, Jan. 2017, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2016.09.023
J.-D. Wu and T.-R. Chen, “Development of a drowsiness warning system based on the fuzzy logic images analysis,” Expert Syst. Appl., vol. 34, no. 2, pp. 1556–1561, Feb. 2008, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2007.01.019
Y. Albadawi, M. Takruri, and M. Awad, “A Review of Recent Developments in Driver Drowsiness Detection Systems,” Sensors, vol. 22, no. 5, art. no. 2069, Mar. 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/s22052069
G. Li and W.-Y. Chung, “Electroencephalogram-Based Approaches for Driver Drowsiness Detection and Management: A Review,” Sensors, vol. 22, no. 3, art. no. 1100, Jan. 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/s22031100
Descargas
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2024 Revista Mexicana de Ingenieria Biomedica

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 4.0.
Una vez que el artículo es aceptado para su publicación en la RMIB, se les solicitará al autor principal o de correspondencia que revisen y firman las cartas de cesión de derechos correspondientes para llevar a cabo la autorización para la publicación del artículo. En dicho documento se autoriza a la RMIB a publicar, en cualquier medio sin limitaciones y sin ningún costo. Los autores pueden reutilizar partes del artículo en otros documentos y reproducir parte o la totalidad para su uso personal siempre que se haga referencia bibliográfica al RMIB. No obstante, todo tipo de publicación fuera de las publicaciones académicas del autor correspondiente o para otro tipo de trabajos derivados y publicados necesitaran de un permiso escrito de la RMIB.











